What If the Village WAS the Investor?
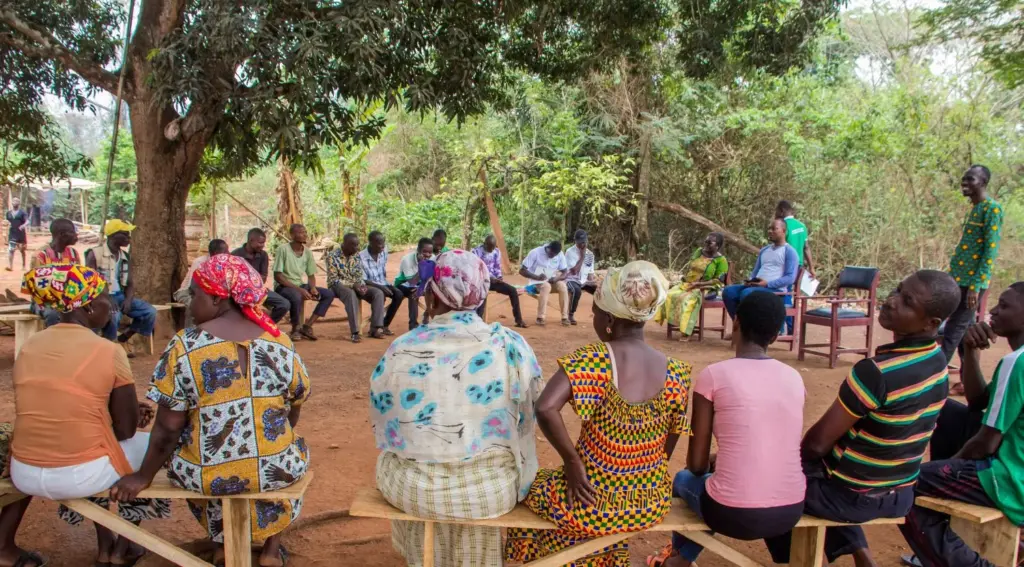
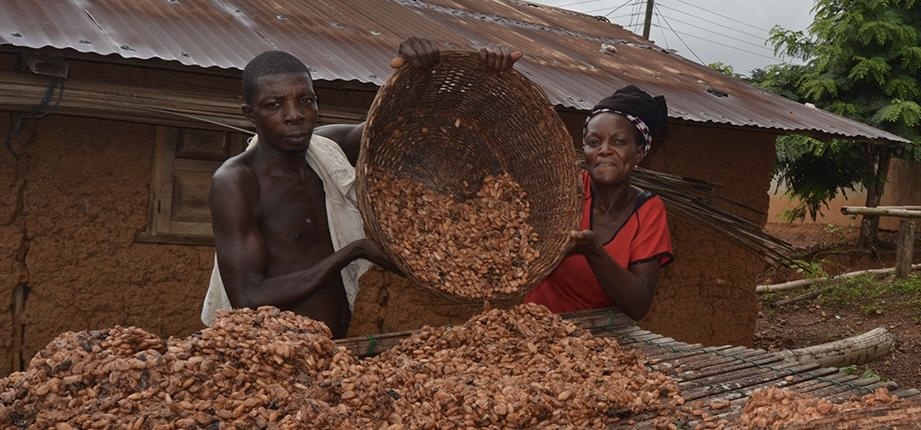
We often discuss attracting investment into rural areas, focusing on agriculture, infrastructure, and essential services. Usually, the conversation revolves around how to draw in urban or foreign capital. Yet, after years working across agriculture, finance, technology, and community empowerment, I found a compelling alternative while writing my last article: What if the village itself was the investor? It’s a practical challenge to the prevailing narrative. A brain-scratcher. I hope to compel us to rethink capital, community participation, and rural agency fundamentally. The Origin of This Question Through my extensive interactions with farmers, traders, processors, local cooperatives, investors, and policymakers, it has become increasingly evident that rural communities often receive minimal benefit despite their vital role in value creation. The pattern remains consistent: villagers bear the risk, supply the labour, and contribute the land, yet they see little financial reward. Why should value always flow towards urban centres while risk remains rooted in rural communities? Perhaps villages possess more hidden economic strength than traditionally acknowledged. It is essential that we explore this untapped potential, recognising villagers not just as recipients but as architects of their economic futures. Reframing the Conversation The dialogue should move from “Who owns the village economy?”, the subject of my previous article, to “What does the village economy own?” This reframing transforms rural residents from passive recipients of aid to active stakeholders. It redefines charitable support as sustainable investment and shifts marginalisation towards strategic economic importance. Imagine if villagers pooled resources through cooperatives and community trusts, investing directly in local or regional enterprises. What if smallholder farmers jointly invested in solar-powered cold storage, boreholes, or technology platforms? Furthermore, community investment could extend into urban ventures, enabling rural capital to flow towards a wider range of potentially profitable opportunities. The aim is not to romanticise local capital but rather to recognise, harness, and strategically deploy it, enabling rural communities to actively participate in wider economic systems. Practical Implementation Models There are viable models to consider, each with significant potential. Pooled Land-Use Trusts: Villages consolidate land into trusts, negotiating stronger collective leasing terms with agribusinesses or developers. Such arrangements ensure ongoing dividends instead of mere rental fees, creating sustainable income sources and strengthening local bargaining power. Community Investment Funds: By shifting traditional contributions from social events (funerals & weddings) into structured investment vehicles, communities can acquire equity stakes in infrastructure projects, local businesses, or diaspora-focused housing. Financial literacy and organised training would enhance this model’s effectiveness. Micro-Equity Infrastructure Ownership: Villages share ownership of infrastructure (e.g., boreholes, energy grids) through micro-equity models, encouraging communal maintenance and allowing revenue from service provision to be reinvested into community development. Promoting local ownership of renewable energy infrastructure could further boost resilience and sustainability. Digital Crowdfunding Platforms: Digital platforms, similar to successful models in Kenya (M-Changa) and Nigeria (Farmcrowdy), can enable direct community investment in agribusinesses or larger enterprises, supporting local and national value chains. Collaborations with fintech firms could accelerate these initiatives, ensuring transparency and easy participation. Also, I need to get me a crowdfunding licence. Global Trends Validating Village-Based Investments Far from being utopian, community-driven investments have demonstrated success worldwide. In the U.S., towns often partially own broadband networks, ensuring fair access and generating local revenues. Farmer cooperatives in Asia successfully handle profitable exports, showcasing rural communities’ capacity to participate effectively in global markets. Latin American indigenous communities have created their own banks and investment funds, fostering economic independence and resilience. These examples demonstrate feasibility, with mobile money and fintech tools increasingly making contributions, tracking, and dividend distribution easier. The existing cash flow in the informal sector, combined with youthful entrepreneurial energy returning to rural areas, further strengthens the business case. Learning from these global examples, Ghana could adopt best practices to fit local contexts and needs. The Business and Economic Case Businesspeople might rightly ask, “What’s the benefit if villages become investors?” Consider the following expanded points. Lower Investment Risks: Local stakeholders with financial interests will safeguard, uphold, and improve their investments, greatly decreasing operational risks. Loyal and Engaged Markets: Communities that invest in products or services become committed consumers, enhancing market sustainability and reliability. Lower Capital Costs: Local contributions can cut reliance on costly bank loans, particularly for medium-scale infrastructure, making the model more financially sustainable. Regulatory and Community Goodwill: Projects with local ownership usually face fewer bureaucratic hurdles and community opposition, making approval processes quicker and timelines shorter. Addressing Potential Challenges Naturally, complexities can emerge. Trust and Fund Management: It can be challenging to ensure transparent, accountable oversight mechanisms, with community-led committees or independent oversight bodies managing investments. Legal Frameworks: Modifying existing legislation to support community-owned financial structures may necessitate collaboration among communities, legal experts, and policymakers. Financial Education and Cultural Shifts: There are barriers to promoting community acceptance and training stakeholders in financial literacy and investment strategies, ensuring ongoing participation. These challenges, however, are solvable design issues rather than insurmountable obstacles, achievable through structured planning and stakeholder engagement. Broader Horizons: What Else Village Investment Unlocks Beyond the clear economic case, there are several often-overlooked areas where community-driven investment can quietly but profoundly shape rural futures. These perspectives are worth serious consideration. Environmental and Climate Resilience: By pooling resources into renewable energy, agroforestry, or water conservation, villages can go green while safeguarding their livelihoods. Community-funded solar microgrids or reforestation efforts can generate income, reduce reliance on external energy sources, and buffer against droughts or floods. It’s long-term thinking, rooted in the land. Diaspora and Rural–Urban Linkages: Many rural families already receive support from relatives in cities or abroad. However, those remittances often flow informally and unpredictably. Transparent, village-level investment platforms can turn that flow into structured support, directed towards boreholes, ICT centres, or agro-processing. The emotional bond already exists. What is needed is clarity, credibility, and coordination. Women and Youth Inclusion: Too often, the same hands hold the reins. But when women and young people lead enterprises, whether it’s shea butter cooperatives, digital services, or poultry farms, you get innovation, adaptability, and fresh energy. And practically speaking, these
What If the Village WAS the Investor? Read More »