The Power of Community in Entrepreneurial Success and Our Call to Action
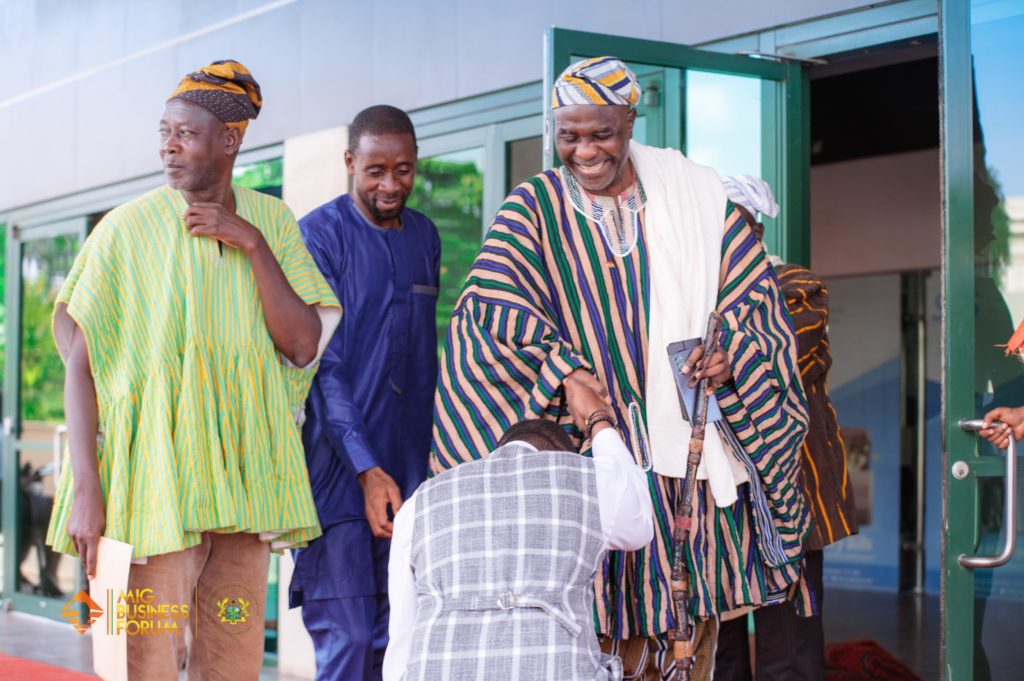
Entrepreneurship is often associated with individualism, risk-taking, and innovation in today’s fast-paced world. While these traits are undoubtedly essential for any successful venture, the critical role of the community in fostering entrepreneurial success must be considered. In reflecting on the recent MIG Business Forum and the exciting initiatives discussed, we want to emphasize the importance of community and extend a humble call to action for everyone to contribute to and benefit from a collaborative, entrepreneurial ecosystem that will be enhanced as we continue to surge forward. COMMUNITY SERVES AS THE BACKBONE OF ENTREPRENEURSHIP FOR SEVERAL REASONS. A Strong Support System One of the primary reasons community is integral to entrepreneurial success is the support system it provides. Entrepreneurship can be a lonely and challenging journey with setbacks and uncertainties. A robust community allows entrepreneurs to share their experiences, learn from one another, and pool resources to tackle challenges. Celebrating Victories Together A supportive community helps entrepreneurs face challenges and celebrates their victories, both big and small. This celebration of success motivates and inspires entrepreneurs, fuelling their passion and drive for their ventures. Additionally, it fosters a sense of belonging and camaraderie, reminding entrepreneurs that they are not alone on their journey. Collaboration and Collective Wisdom Another key benefit of a robust entrepreneurial community is the opportunity for collaboration and the pooling of collective wisdom. Entrepreneurs who are part of a community can tap into their fellow members’ diverse skills, experiences, and perspectives, generating new ideas and finding innovative solutions to problems. Collaboration can also lead to strategic partnerships, helping businesses to grow and expand their reach. Embracing Diversity and Inclusivity Diversity and inclusivity are vital components of a community-driven entrepreneurial ecosystem. We create a dynamic environment that encourages creativity and positive change by welcoming individuals from different backgrounds, industries, and perspectives. A diverse community generates new ideas, challenges established paradigms, and leads to unique solutions that cater to a broader audience. The Ripple Effect of a Supportive Community The positive impact of a strong community extends far beyond the entrepreneurs themselves. By fostering an environment where entrepreneurship can flourish, communities can experience significant economic growth and job creation. Moreover, a thriving entrepreneurial ecosystem can inspire future generations, instilling a culture of innovation and ambition that spans generations. UNLEASHING THE POTENTIAL OF ENTREPRENEURSHIP: KEY INITIATIVES FROM THE MIG BUSINESS FORUM The recent MIG Business Forum showcased a range of initiatives designed to harness the power of the community and propel entrepreneurship forward. These are the Soya Beans & Agro-Commodities Project, the Useful Affordable Education Drive in partnership with KNUST-AISWAM, the Community Insurance Project in collaboration with Cosmopolitan Health Insurance, activating the Ghanaian Bamboo Industry with a ready market and processing capacity, and the Maxwell Homes Project. By focusing on innovation, education, skill development, wealth via health, and sustainability, these initiatives have the potential to transform the entrepreneurial landscape and create lasting, positive change in our communities. One key initiative discussed at the Forum was the establishment of collaborative economic clusters for entrepreneurs to work, network, and share ideas, suggested by world-renowned Economist Naa Dr Alhassan Andani. He is a former Director/CEO of Stanbic Bank Ghana and enskinned as the chief of Pishigu in the Northern Region of Ghana. These economic clusters can act as incubators for innovation, helping entrepreneurs bring new concepts to life and fostering a culture of creativity within the community. By providing resources, guidance, and support, these spaces can also help entrepreneurs overcome the challenges they may face in the early stages of their ventures. Yet another vital aspect of the Forum’s initiatives was the emphasis on education and skill development. By educational courses from KNUST that are useful, affordable and productive, these programs will be tailored to the needs of entrepreneurs and the community and ensure that its members have access to the knowledge and skills required for success in the ever-evolving business landscape. In addition, this focus on education empowers individual entrepreneurs and contributes to the community’s overall competitiveness and resilience. This is why all those that complete the courses under this Project will receive a KNUST-accredited certificate, signed by the Vice Chancellor, giving course participants a competitive edge in the job markets. Sustainability was another central theme at the MIG Business Forum, with several projects aiming to create environmentally friendly and socially responsible business opportunities. By encouraging the development of sustainable enterprises, the community can contribute to long-term economic growth and environmental stewardship. In addition, these initiatives can also promote inclusive growth by ensuring that benefits are distributed equitably among community members, regardless of their socioeconomic background. To guarantee the success of these initiatives, we must all play our part in supporting and participating in them. By working together, we can create a vibrant, thriving entrepreneurial community that drives positive change and delivers lasting benefits for all its members. You can see pictures and complete coverage of the recent MIG Business Forum here; www.bit.ly/MBFv1 CALL TO ACTION: CONTRIBUTING TO A COLLABORATIVE ECOSYSTEM The initiatives discussed at the recent MIG Business Forum exemplify how community collaboration can advance entrepreneurship. To ensure the success of these initiatives, we all must take an active role in supporting and participating in them. Here are some ways you can contribute to a collaborative, entrepreneurial ecosystem: THE TRANSFORMATIVE POWER OF COMMUNITY COLLABORATION Embracing the power of community is essential for realizing the full potential of entrepreneurship. This often-underappreciated aspect is critical in fostering a vibrant, inclusive, and supportive ecosystem, contributing to entrepreneurial success. By working collaboratively and engaging in shared initiatives, we can create lasting, meaningful change in the lives of many individuals. Now is the time to seize this opportunity, transforming our collective vision into reality and stepping forward with a unified purpose. By doing so, we can significantly impact our society, economy, and the world at large. I hope you found this article insightful and enjoyable. Subscribe to the ‘Entrepreneur In You’ newsletter here: https://lnkd.in/d-hgCVPy. I wish you a highly productive and successful week ahead! ♕ —- ♕ —- ♕ —- ♕ —- ♕ Disclaimer: The views, thoughts, and
The Power of Community in Entrepreneurial Success and Our Call to Action Read More »