Depression and Cultural Perception of Mental Health in Africa.
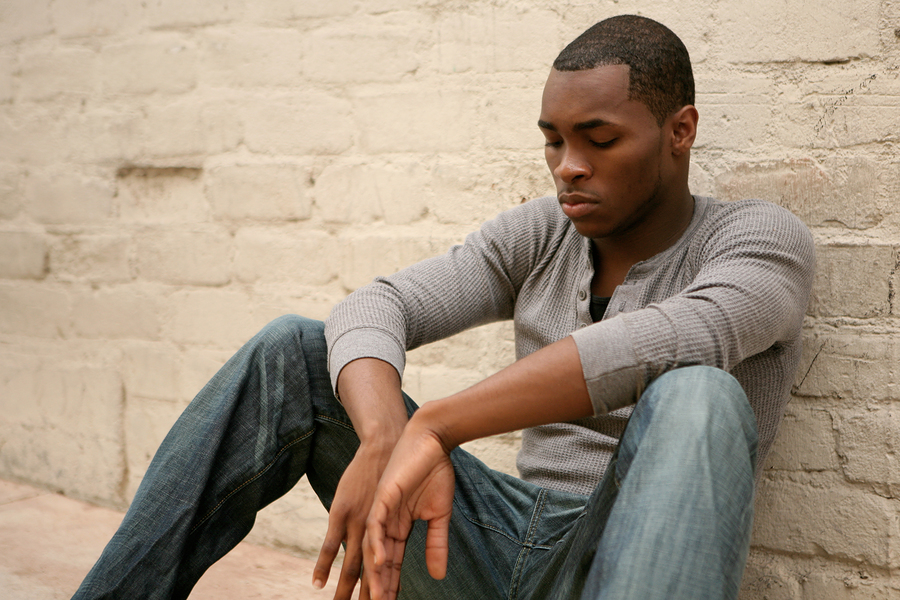
The Unseen Barrier to Economic Progress Africa, often hailed as the continent of the future, boasts a young and dynamic population. Yet, this potential is being stifled, not just by infrastructure gaps or political instability, but by a more insidious, often-overlooked issue: mental health neglect. Depression and anxiety are not just personal battles; they are economic drains that hinder productivity, innovation, and growth. If we fail to address this, we risk squandering Africa’s greatest asset: our people. The Economic Impact of Mental Health Neglect Mental health disorders are more than medical concerns. They have tangible economic repercussions: – Lower Workforce Productivity: Depression reduces an employee’s ability to focus, collaborate, and perform efficiently. According to the World Health Organization, untreated depression and anxiety result in lost productivity worth $1 trillion globally each year. – Increased Healthcare Burden: When mental health issues remain untreated, they contribute to physical health problems such as heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure, further straining national healthcare systems. – Higher Unemployment Rates: Many individuals suffering from depression struggle to hold stable employment, increasing dependency on the public purse. The Mental Health Crisis in Africa: The Hard Facts According to the World Economic Forum, Africa is home to 100 million people suffering from clinical depression, including 66 million women. Yet, the region is ill-equipped to handle this crisis: – A severe shortage of mental health professionals: Only 1.4 mental health workers per 100,000 people, compared to a global average of nine per 100,000 (Lancet Global Health). – A staggering treatment gap: In Ghana, for example, 98% of people needing mental health services do not receive treatment (Harvard Global Health Institute). – Minimal government funding: Many African nations allocate less than 1% of their health budgets to mental health. Why Mental Health Matters for Africa’s Future Ignoring mental health is not an option if Africa is to achieve its economic aspirations. Addressing it will lead to the following: – A More Productive Workforce: Healthy minds lead to sharper decision-making, higher efficiency, and increased economic participation. – Stronger Entrepreneurial Growth: Africa’s entrepreneurial ecosystem thrives on innovation and resilience, both of which require a strong mental foundation. – Increased Foreign Investment: Stable, productive societies attract investors looking for long-term returns. The Hidden Costs of Ignoring Mental Health Failure to act on mental health comes at a steep price: – Missed economic opportunities: Depression alone is estimated to cost Africa millions of productive work hours annually. – Rising social instability: Unaddressed mental health issues contribute to crime, substance abuse, and social unrest. – A struggling next generation: Poor mental health among today’s workforce affects families, leading to cycles of poverty and despair. The Role of Corporate Responsibility in Mental Health Companies and organisations are crucial in tackling Africa’s mental health crisis. Here’s how they can contribute: – Implementing Mental Health Support Programs: Businesses should integrate Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) that offer mental health support services, counselling, and stress management workshops. – Fostering a Workplace Culture That Supports Well-being: Employers should encourage open discussions about mental health, reducing stigma and making employees feel safe when seeking help. – Offering Flexible Work Arrangements: Allowing flexible schedules and remote work options where possible can help employees manage stress more effectively. – Providing Mental Health Training for Managers: Managers should be trained to recognise early signs of mental distress and guide employees to appropriate resources. Investing in mental health is ethical and financially smart. Companies that prioritise mental well-being often report higher employee satisfaction, lower turnover rates, and increased productivity. The Cultural Perception of Mental Health in Africa One of the biggest barriers to mental health awareness in Africa is deep-rooted stigma. In many African societies, mental health issues are often misunderstood, with sufferers facing judgment, discrimination, or even ostracisation. – Traditional Beliefs and Mental Health: Many cultures attribute mental illnesses to supernatural causes, spiritual possession, or moral weakness, which prevents people from seeking professional help. – Lack of Awareness: In some communities, depression and anxiety are dismissed as mere mood swings rather than severe medical conditions. – Fear of Social Consequences: People hesitate to admit mental health struggles due to fear of losing their jobs, reputations, or relationships. Changing the Narrative To shift this mindset, we need to: – Promote Public Awareness Campaigns: Governments and NGOs should run campaigns to educate the public about mental health and reduce misinformation. – Engage Religious and Community Leaders: Since many African societies rely on traditional and religious guidance, working with these leaders to promote mental health awareness can be impactful. – Integrate Mental Health Education into Schools: Teaching young people about mental well-being can help normalise the conversation from an early age. The Role of Technology in Bridging the Gap With traditional healthcare systems unable to meet demand, technology offers promising solutions: – Mobile Mental Health Apps: Platforms like MindIT provide therapy, meditation tools, and self-help resources to individuals with limited access to in-person services. – AI-Driven Chatbots: Digital assistants can provide mental health screenings and immediate support. – Online Therapy Platforms: Connecting individuals with mental health professionals through virtual consultations reduces geographic barriers. A Movement to Change the Narrative Recognising the urgency of this issue, a new initiative seeks to blend mental health awareness with professional development. Through LinkedIn LIVE discussions, expert panels, and interactive sessions, this movement aims to: – Challenge the stigma surrounding mental health in Africa. – Provide tangible solutions for business leaders, employees, and entrepreneurs. – Foster collaboration between policymakers, corporations, and health experts. How You Can Be Part of the Solution This is not just a call to awareness; it is a call to action! Here’s how you can help: – Join the Conversation: Share your insights on mental health in the workplace. – Sponsor the Initiative: Help fund the expansion of mental health resources. – Spread Awareness: Share this project within your networks. – Be a Speaker: Contribute your expertise and lived experiences to the dialogue. The Time for Change is Now Mental health is not a luxury. It is a fundamental requirement for economic progress. Africa cannot afford to ignore this issue any longer. By tackling depression and related challenges, the continent can unlock billions in lost productivity, empower
Depression and Cultural Perception of Mental Health in Africa. Read More »