Local agroeconomic clusters play a crucial role in the growth and sustainability of regional economies. Moreover, by focusing on local buyers, these clusters can create a ripple effect of benefits that extends beyond the businesses themselves, touching the lives of countless individuals within the community.
I want to explore ten compelling reasons local agroeconomic clusters should prioritise local buyers. By understanding the advantages of engaging local buyers, businesses can create a more inclusive, vibrant, and prosperous ecosystem that benefits everyone involved.
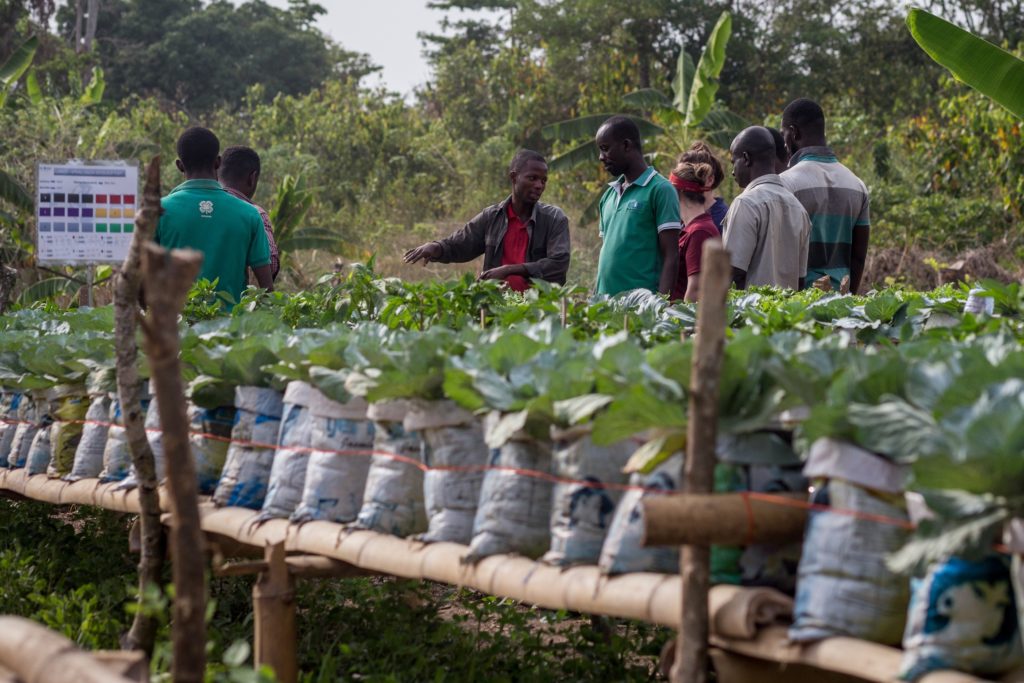
Local companies in this regard can be agro-sector players like Maxwell Investments Group or multinational giants like WILMAR Ghana, which have and continue to invest hundreds of millions of dollars into local manufacturing, hiring hundreds of workers and feeding, by extension, thousands of households indirectly, while engaging in outreach programs, affecting the lives of millions within the walls of Ghana.
Here are ten reasons why local agroeconomic clusters should choose local buyers:
1. STRENGTHENING LOCAL ECONOMIES: Engaging local buyers is pivotal in circulating money within the community, contributing to a stronger and more resilient local economy. When local agroeconomic clusters prioritise local buyers, they directly impact various aspects of the regional economy.
a. Job creation: Local companies generate employment opportunities for the local population, from production and distribution to sales and marketing. This not only reduces unemployment rates but also fosters economic stability and growth.
b. Supporting local suppliers: By prioritising local buyers, businesses are more likely to source raw materials, products, and services from within the community. This support boosts the economic prospects of local suppliers and encourages the development of a robust and diverse supplier network. This strengthens the entire value chain, benefiting all stakeholders involved.
c. Investment in community development projects: Companies prioritising local buyers often invest in community development initiatives, ranging from infrastructure projects to education and healthcare programs. These investments improve community members’ quality of life and create a more attractive environment for further business and investment. For example, WILMAR’s outreach programs and investments in Ghana have significantly impacted the lives of millions. So has the ‘Useful, Affordable Education Drive’ and the ‘Insurance Community Project’, amongst others, from Maxwell Investments Group.
d. Economic multiplier effect: When local businesses engage local buyers, a multiplier effect is created as money spent within the community gets circulated and reinvested. This means every cedi paid at a local business generates additional income for other local companies and individuals, leading to a more prosperous and self-sufficient local economy.
e. Building a resilient local economy: By strengthening local supply chains and creating a network of local buyers and suppliers, businesses develop a more resilient economy better equipped to withstand external shocks and uncertainties. This resilience ultimately benefits the country by ensuring the local economy can recover quickly from adverse events or market fluctuations.
Engaging local buyers is instrumental in strengthening local economies by creating job opportunities, supporting local suppliers, investing in community development projects, generating economic multiplier effects, and building a more resilient financial ecosystem. Companies like Maxwell Investments Group and WILMAR are prime examples of how prioritising local buyers can have a lasting and transformative impact on their communities.
2. BUILDING COMMUNITY RELATIONSHIPS: Prioritising local buyers enables businesses to establish and nurture more robust relationships with community members, which is crucial for long-term success. The various aspects of building community relationships through engaging local buyers include:
a. Fostering trust: By supporting local buyers, businesses demonstrate their commitment to the community’s well-being, which helps build trust between the business and community members. This trust is vital for the company’s long-term success and fosters a healthy business environment.
b. Enhancing loyalty: When businesses prioritise local buyers, they invest in the community’s future and show they care about its success. This commitment cultivates customer loyalty, resulting in repeat business, positive word-of-mouth, and increased customer retention.
c. Encouraging a sense of belonging: Engaging with local buyers fosters a sense of belonging within the community. When people feel connected to a business, they are more likely to support and recommend it to others. This sense of belonging can contribute to a more cohesive and supportive community.
d. Expanding networks: By prioritising local buyers, businesses can expand their network of customers, suppliers, and other stakeholders within the community. These relationships can lead to new business opportunities, strategic partnerships, and collaborations that drive growth and innovation.
e. Facilitating knowledge exchange: When businesses engage local buyers, they create knowledge exchange and learning opportunities. This can result in the sharing of ideas, best practices, and expertise, ultimately contributing to the overall growth and development of the community.
f. Promoting local culture and identity: Businesses can help preserve and promote local culture and identity by engaging local buyers. This, in turn, can contribute to a stronger sense of pride and unity within the community, which can positively affect the overall social and economic well-being of the region.
Prioritising local buyers allows businesses to build strong community relationships by fostering trust, enhancing loyalty, encouraging a sense of belonging, expanding networks, facilitating knowledge exchange, and promoting local culture and identity. These strengthened relationships contribute to a supportive and prosperous community where businesses and residents can thrive.
3. ENHANCING LOCAL SUPPLY CHAIN RESILIENCE: Prioritising local buyers bolsters businesses by reducing dependence on global suppliers and mitigating risks linked to supply chain disruptions. This leads to a more resilient local economy with numerous advantages:
a. Adaptability: Local supply chains can rapidly react to market changes, ensuring businesses can maintain operations during unexpected situations. This adaptability enables companies to stay competitive and adjust their strategies as needed.
b. Collaboration: Establishing solid relationships within local supply chains fosters collaboration, knowledge sharing, and innovation. These partnerships can result in improved products and services and new solutions to meet market demands.
c. Sustainability: Local supply chains often have a smaller environmental footprint, supporting sustainable business practices that benefit the community and the planet and promoting environmentally responsible practices.
d. Economic diversification: A resilient local supply chain encourages economic diversification, allowing businesses to explore new markets and opportunities within the community. This diversification can create jobs and a more stable regional financial foundation.
By investing in local supply chain resilience, businesses and communities are better prepared to face challenges and uncertainties while fostering regional economic growth and stability.
4. ENCOURAGING LOCAL INNOVATION: Prioritising local buyers drives innovation within the community, as businesses are well-positioned to comprehend and cater to their customers’ distinct needs and preferences. This leads to the creation of novel products, services, and business models that address the unique demands of the local market. Several benefits arise from this:
a. Customer-centric approach: By understanding local customers’ needs, businesses can develop tailored solutions, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty. This customer-centric approach can result in a competitive advantage and long-term success.
b. Knowledge sharing: Engaging local buyers facilitates the community’s exchange of ideas and knowledge. This transfer of information and expertise can accelerate the development of innovative solutions and foster a culture of collaboration and continuous improvement.
c. Niche market opportunities: Businesses can identify niche markets and untapped opportunities within the community by focusing on local buyers. This can lead to development of specialised products and services that cater to these unique needs, expanding the company’s customer base and revenue potential.
d. Adaptability and agility: Local businesses that prioritise their community’s needs and innovate to the specific needs of their community are often more agile and adaptable to market changes. They can quickly respond to emerging trends, regulatory shifts, or new customer demands, ensuring long-term viability and success.
By encouraging local innovation, businesses can contribute to the growth and prosperity of their community, creating new opportunities and solutions that directly benefit those around them.
5. REDUCING ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACTS: By focusing on local buyers, businesses can source and sell products locally, which helps minimise the environmental impacts of transportation and logistics. This approach offers several advantages:
a. Lower emissions: By reducing the distance that goods need to travel, businesses can decrease their carbon footprint, contributing to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and combatting climate change.
b. Sustainable resource management: Local sourcing can promote more sustainable resource management practices, as businesses can directly collaborate with suppliers to ensure responsible production methods and resource use.
c. Reduced packaging and waste: When goods are sourced and sold locally, there is often a reduction in packaging materials required for transport, leading to less waste generation and a smaller environmental footprint.
d. Supporting local eco-friendly initiatives: By engaging local buyers, businesses can support and promote local eco-friendly initiatives, such as community gardens, farmers’ markets, and sustainable agriculture practices. This helps to create a more environmentally conscious and sustainable community.
By minimizing their environmental impacts, businesses can contribute to a greener future and appeal to increasingly environmentally conscious consumers, who often prioritize sustainable products and practices. This can lead to enhanced brand reputation and customer loyalty.
6. PRESERVING AND PROMOTING LOCAL CULTURE AND TRADITIONS: By supporting local businesses and artisans, community members help keep traditional crafts, techniques, and knowledge alive, which might otherwise be lost.
a. Community identity and pride: A strong local culture contributes to a sense of identity and pride within the community. By purchasing from local businesses, individuals support their region’s unique aspects, fostering a sense of belonging and cohesion among community members.
b. Attracting tourism: When local culture and heritage are preserved, regions become more attractive to tourists interested in experiencing the unique aspects of the area. This can lead to increased revenue from tourism and a positive reputation for the region and the economic clusters.
c. Celebrating diversity: By promoting local culture, businesses help celebrate the diversity that exists within the community. This can lead to increased understanding, tolerance, and appreciation for different perspectives and ways of life, enriching the community.
By engaging local buyers and preserving local culture, businesses can contribute to a thriving, diverse, resilient community proud of its heritage and traditions.
7. FASTER FEEDBACK AND ADAPTATION: Engaging local buyers offers businesses within clusters a distinct advantage when receiving feedback and adjusting their operations accordingly. This can be seen through the following subpoints:
a. Direct communication: Local buyers have more opportunities to interact directly with businesses through face-to-face interactions or local social media platforms. This direct communication allows for real-time feedback, making it easier for companies to understand the needs and preferences of their customers.
b. Market responsiveness: By obtaining immediate feedback from local buyers, businesses can make informed decisions about the direction of their products and services. This responsiveness helps companies to stay competitive in their market, as they can quickly adapt to changing trends, preferences, and requirements.
c. Continuous improvement: Regular feedback from local buyers enables businesses to identify areas of improvement, whether in product quality, customer service, or overall operations. This continuous feedback cycle and adaptation ensure that companies strive for excellence, benefiting the business and the local community.
d. Tailored products and services: When businesses deeply understand their local customers’ needs and desires, they can create products and services tailored to meet those requirements. This customization can increase customer satisfaction and loyalty and sales, and revenue.
By engaging local buyers and prioritising their feedback, businesses within agroeconomic clusters can benefit from faster adaptation and improvement, ensuring they remain agile and responsive to the ever-changing market landscape.
8. SUPPORTING LOCAL ENTREPRENEURSHIP: Focusing on local buyers benefits established businesses and helps nurture a thriving entrepreneurial ecosystem within the community. This can be observed through the following subpoints:
a. Mentorship and knowledge sharing: When established businesses within a cluster engage with local buyers, they can share their expertise and mentor aspiring entrepreneurs. This exchange of knowledge and experience fosters an environment conducive to the growth of new businesses and ideas.
b. Access to resources: Engaging local buyers can increase local entrepreneurs’ visibility and connections. This can result in more accessible access to essential resources, such as funding, suppliers, and skilled labour, which are crucial for the success of new businesses.
c. Stimulating competition: A robust entrepreneurial ecosystem that engages local buyers can encourage healthy competition within the community. This competitive environment can drive innovation and improvements in products and services, ultimately benefitting both businesses and their customers.
d. Creation of jobs and economic growth: As more entrepreneurs establish businesses within the community, job opportunities increase, leading to a more robust local economy. This economic growth can have positive ripple effects throughout the community, improving living standards and a higher quality of life.
By prioritizing local buyers, clusters can play a vital role in fostering a thriving entrepreneurial ecosystem, ultimately leading to increased job opportunities, economic growth, and a more diverse and resilient local economy.
9. ENHANCING SOCIAL COHESION: Prioritising local buyers can contribute significantly to building community and social cohesion within the region. This can be observed through the following subpoints:
a. Shared values and interests: When businesses engage with local buyers, they can better align their products and services with the values and interests of the community. This fosters a sense of belonging and unity among community members, as they can identify with the businesses and feel that their needs and preferences are being considered.
b. Trust and loyalty: Engaging local buyers can help establish trust between businesses and community members. This trust can increase loyalty and long-term support for local companies, as people are likelier to choose familiar and trustworthy establishments over distant or unknown alternatives.
c. Community involvement: Businesses prioritising local buyers often have a vested interest in the community’s well-being. This can result in greater participation in local events, sponsorship of community initiatives, and collaboration with other organizations to address shared challenges, further enhancing social cohesion.
d. Social capital: By engaging local buyers, businesses can contribute to building social capital within the community. This includes fostering networks of relationships, trust, and cooperation among community members, which can lead to increased collaboration and collective action to address common issues or achieve shared goals.
Through these various factors, engaging local buyers can help to create a strong sense of community and social cohesion, contributing to overall social stability and harmony within the region.
10. GENERATING LOCAL MULTIPLIER EFFECTS: Focusing on local buyers can generate significant multiplier effects within the community, ultimately benefiting the local economy. This can be observed through the following subpoints, some of which might seem to be iterated earlier. Still, the main idea is to fixate on the multiplier effect capacity of doing agribusiness with local buyers:
a. Recirculation of income: When local businesses cater to local buyers, their revenue is more likely to be re-spent within the community. This recirculation of revenue helps support other local businesses, suppliers, and service providers, creating a continuous cycle of economic activity that strengthens the local economy.
b. Job creation: As local businesses thrive, they often expand their operations and hire additional staff. This creates new job opportunities within the community, leading to increased local employment and reduced unemployment rates.
c. Indirect benefits: The multiplier effect goes beyond the immediate beneficiaries of the increased spending. For example, when a local business experiences growth, it may require more products or services from local suppliers, creating more demand for its goods and services. This indirect benefit can extend through multiple layers of the local economy, stimulating growth and development across various sectors.
d. Increased tax revenue: When local businesses experience growth due to increased demand from local buyers, they often generate more revenue. This can lead to increased tax contributions, which local governments can use to fund infrastructure projects, public services, and other initiatives that benefit the community.
By focusing on local buyers, businesses can generate multiplier effects that have far-reaching benefits for the community, ultimately stimulating economic activity, job creation, and overall regional development.
In conclusion, prioritising local buyers in local agro-economic clusters is essential for creating thriving, resilient communities. Local agro-buyers such as Maxwell Investments Group and even giants like WILMAR are better positioned to contribute to social, economic, and environmental sustainability in their communities by focusing on local engagement. This approach fosters innovation, strengthens supply chain resilience, and generates positive multiplier effects, benefiting the community.
As businesses understand and embrace the importance of engaging local buyers, they can nurture strong relationships with community members, creating a foundation of trust and loyalty. This, in turn, leads to increased collaboration, social cohesion, and a shared sense of responsibility for the community’s well-being.
By prioritising local buyers, businesses can create a more inclusive, resilient, and prosperous environment that benefits everyone involved. The long-term success of agro-economic clusters depends on the strategic integration of local engagement into their business models, ensuring that the benefits of their activities are felt within the communities they serve.
♕ —- ♕ —- ♕ —- ♕ —- ♕
I hope you found this article insightful and enjoyable. Subscribe to the ‘Entrepreneur In You’ newsletter here: https://lnkd.in/d-hgCVPy.
I wish you a highly productive and successful week ahead!
♕ —- ♕ —- ♕ —- ♕ —- ♕
Disclaimer: The views, thoughts, and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the author, Dr. Maxwell Ampong, and do not necessarily reflect the official policy, position, or beliefs of Maxwell Investments Group or any of its affiliates. Any references to policy or regulation reflect the author’s interpretation and are not intended to represent the formal stance of Maxwell Investments Group. This content is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal, financial, or investment advice. Readers should seek independent advice before making any decisions based on this material. Maxwell Investments Group assumes no responsibility or liability for any errors or omissions in the content or for any actions taken based on the information provided.